First, Second, or Third-Degree? How to Identify Burn Injuries and What to Do Next
Share:
Burn injuries are among the most painful and traumatic experiences a person can endure—and they can happen anywhere, from a kitchen accident to a workplace incident or vehicle fire. While some burns are minor and heal quickly, others can lead to permanent disfigurement, disability, or even death.
Whether you’re a burn injury victim, a concerned loved one, or just want to be better informed, this guide will walk you through the different types of burn injuries, their most common causes, and the treatment options available. Our goal? To help you understand your rights, recognize the severity of a burn, and make informed decisions when it matters most.
What Are Burn Injuries?
A burn injury is damage to the skin—or deeper tissues—caused by heat, chemicals, electricity, sunlight, or radiation. According to the American Burn Association, nearly 500,000 burn injuries receive medical treatment in the U.S. each year. While many are treatable, the severity of a burn significantly impacts recovery time and the risk of complications.
Types of Burn Injuries
Burns are classified by degrees, which indicate the depth and severity of the damage. Here’s what you need to know:
First-Degree Burns (Superficial Burns)
These affect only the outer layer of the skin (epidermis).
- Symptoms: Redness, mild swelling, pain, no blistering.
- Common Causes: Sunburns, brief contact with hot objects or liquids.
- Treatment: Cool water, aloe vera, over-the-counter pain relievers. Typically heals within 3–7 days without scarring.
➡️ Example: Touching a hot pan briefly or spending too much time in the sun without protection.
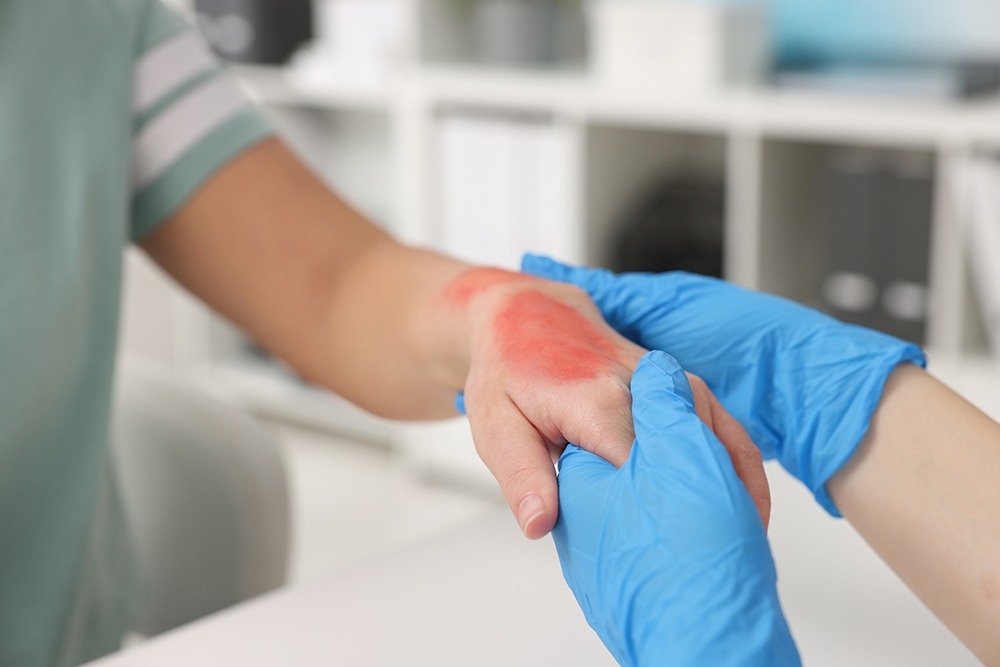
Second-Degree Burns (Partial-Thickness Burns)
These extend into the second layer of skin (dermis).
- Symptoms: Red or blotchy skin, blisters, severe pain, swelling.
- Common Causes: Scalds from hot liquids, flash burns from gasoline or chemicals.
- Treatment: May require medical treatment, wound care, prescription ointments, and possibly skin grafts. Healing can take 2–3 weeks or longer.
➡️ Key Insight: Second-degree burns can become infected if not properly treated, and they often leave scars if the burn is deep.
Third-Degree Burns (Full-Thickness Burns)
These destroy both the epidermis and dermis, sometimes reaching muscles, tendons, or bones.
- Symptoms: White, blackened, or charred skin; leathery texture; little or no pain due to nerve damage.
- Common Causes: Prolonged exposure to fire, electrical burns, contact with corrosive chemicals.
- Treatment: Emergency medical care, surgery, skin grafting, rehabilitation. Scarring and long-term disability are common.
➡️ Important: Third-degree burns are medical emergencies. Call 911 immediately if someone experiences this type of burn.
Common Causes of Burn Injuries
Burns can occur in countless settings, but some scenarios are more frequent than others. Here are the most common causes:
- Electrical burns: Often from faulty wiring, exposed outlets, or workplace hazards.
- Chemical burns: From exposure to industrial cleaning agents, acids, or alkalis.
- Thermal burns: Caused by contact with flames, steam, or hot surfaces.
- Explosions and vehicle fires: Common in motor vehicle accidents or industrial accidents.
- Radiation burns: Often the result of sun exposure or medical treatments (like radiation therapy).
➡️ Did you know? According to the CDC, children and older adults are at the highest risk for serious burn injuries, particularly in home environments.
Burn Treatment Options: What Are Your Choices?
The right treatment depends on the type, location, and severity of the burn. Here’s a general breakdown of treatment options:
Immediate First Aid
- Remove the person from the source of the burn.
- Cool the burn with lukewarm water (not ice).
- Remove tight clothing or jewelry near the burned area.
- Cover with a clean, non-stick bandage.
Medical Treatments
- Topical antibiotics to prevent infection.
- IV fluids for hydration and stabilization.
- Debridement (removal of dead tissue).
- Skin grafts in severe cases.
- Rehabilitation therapy to restore mobility and function.
Long-Term Care & Legal Options
For victims of severe burn injuries, long-term care may involve:
- Reconstructive surgery
- Physical and occupational therapy
- Psychological counseling for trauma recovery
And if the burn was caused by someone else’s negligence—such as a defective product, unsafe workplace conditions, or a car accident—legal compensation may be available.
Real-World Example
Case in Point: A Florida construction worker suffered second- and third-degree burns due to a malfunctioning industrial machine. After months of recovery and physical therapy, he filed a personal injury lawsuit against the equipment manufacturer. The case resulted in a six-figure settlement, which covered his medical expenses, lost wages, and ongoing care.
Your Rights Matter
If your burn injury was caused by another party’s negligence, you may be entitled to compensation. This includes:
- Medical costs
- Pain and suffering
- Lost income or reduced earning capacity
- Long-term care and rehabilitation
Final Takeaways
- First-degree burns are minor but painful. Treat at home unless they cover a large area.
- Second-degree burns are serious and require medical attention.
- Third-degree burns are life-threatening and need emergency care.
- Know your treatment options, and don’t ignore emotional recovery.
- If the burn was caused by someone else, speak to an attorney about your legal rights.
Get the Legal Help You Need After a Burn Injury
At DuFault Law, we understand how devastating burn injuries can be—physically, emotionally, and financially. Our experienced personal injury team is here to fight for the compensation and care you deserve.
Call (239) 422-6400 or email contact@dufaultlaw.com to schedule your consultation. Let’s take the first step toward healing—together.


Comments are closed